EXPLOSION PROTECTION
Explosion Protection
Whether you’re building a new facility or making changes to an existing process, DenTech can help you integrate appropriate measures to manage combustible dust.
What is explosion protection?
Explosion protection uses mitigation devices (such as ignition controls or explosion vents) and dust collection system design to reduce the chances of a deflagration or explosion caused by combustible dust.
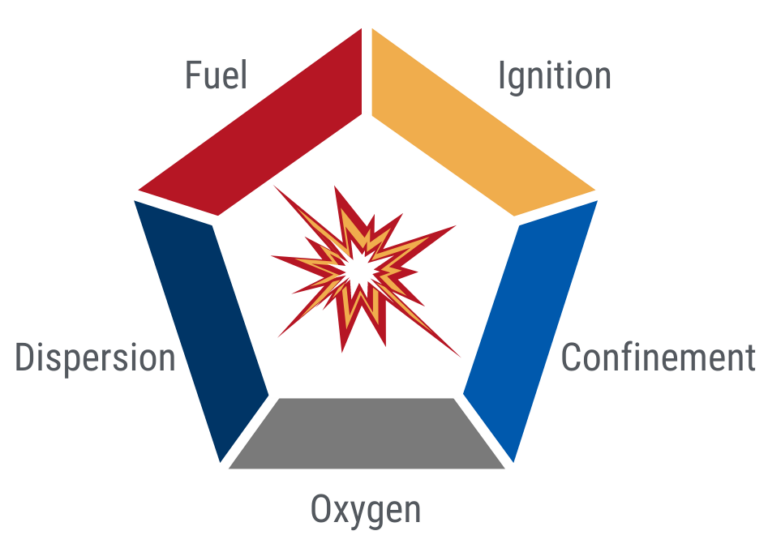
- Ignition (spark or ember)
- Fuel (combustible dust)
- Oxidizer (oxygen in the air)
- Dispersion (dust suspended in the air)
- Confinement (dust concentrated in a small space)
Explosion protection methods may work to prevent incidents or limit the damage caused by incidents.








Why is explosion protection important?
Many manufacturing processes produce small dust particles which may become airborne and settle on various surfaces in the facility. If the dust is combustible, then it could create a potentially explosive dust cloud when disturbed.
Combustible dust presents fire and explosion risks, so manufacturing facilities should take actions to mitigate these risks and keep employees safe. Industries with combustible dust hazards include agriculture, chemical, food, grain, plastics, wood, textiles, metal processing, and pharmaceuticals.
Local, state, and federal mandates apply to facilities to ensure they are operating safely. Many authorities reference standards from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) to identify potential hazards and put proper protections in place.
- NFPA Standard 652: Standard on the fundamentals of combustible dust; includes requirement for dust hazard analysis (DHA)
- NFPA Standard 61: Standard for the prevention of fires and dust explosions in agricultural and food processing facilities
- NFPA 68: Venting of deflagrations
- NFPA 69: Explosion prevention systems
- NFPA 484: Standard for combustible metals
- NFPA: 654: Standard for the prevention of fires and dust explosions in manufacturing and processing facilities
- NFPA 655: Standard for prevention of sulfur fires and explosions
- NFPA: 664: Standard for the prevention of fires and explosions in wood processing and woodworking facilities
Examples of mitigation devices for explosion protection:
In the event of a deflagration, these vents rupture at a specific pressure to minimize damage and direct the fireball and pressure into a safe area.
This vent relieves pressure and includes a steel mesh to contain the flames. Flames are extinguished instead of moving outside the vessel. Steam may escape from the vent.
In the event of a deflagration, the isolation valve will close and block the pressure wave from moving back through the ductwork, into the building, and into workers’ areas.
These devices monitor the system for conditions that indicate a potential explosion, such as a sharp increase in pressure over a short amount of time. The detector sends a signal to selected explosion protection or suppression devices.
When an emerging explosion is detected, the suppression tank receives a switching signal and rapidly releases pressurized extinguishing agent into the protected area.
Examples of fire protection devices:
A spark arrestor is a passive fire protection device that is connected to ductwork in dust collection systems. Plates within the spark arrestor cause air turbulence. When sparks enter the spark arrestor, the turbulence slows them down, so they lose heat.
CO2 systems suppress or extinguish a fire by releasing CO2 into the protected area to reduce the oxygen level to a point where combustion cannot occur. Because CO2 is a gas, there’s no residue or clean-up after the system discharges. This makes CO2 systems ideal to use in place of water sprinklers when the environment has sensitive equipment, such as server rooms, engine rooms, or data centers. But since high concentrations of CO2 are hazardous to humans, CO2 systems are used only in areas that are not occupied by people.
Kidde offers High Pressure CO2 systems and optional smoke detectors as standardized packages to be used with Donaldson Torit dust collectors.
The TG series is designed for thermally generated dust, such as in metal fabrication applications. The TG series offers many benefits including an energy savings, quiet motor, smart controls, smart filter cleaning, filter packs that are easy to change out, and high performance flame-retardant Ultra-Web® filter media.
Firetrace™ systems have specially designed tubing to automatically detect fire at the source. The system activates to release clean chemical agents that are safe for people, equipment, and the environment. Firetrace systems are independent of power, water, and electricity, which makes them ideal for use with high-risk equipment, like CNC machines, electrical cabinets, vehicles, and data centers.
The compressed air dump valve ensures pneumatic components are exhausted and de-energized as quickly as possible in an e-stop situation. Exhausting the compressed air from the system prevents further machine movements. Compressed air dump valves are an add-on for the AyrDyne monitoring system HMI
How DenTech Can Help
As a systems integrator, DenTech does more than buy parts. We’ll develop a custom solution that fits with your facility’s system and processes.
We’ll start with identifying combustible dust hazards in your facility. After reviewing your dust collection system, we’ll recommend improvements and mitigation devices for your production process.
Turnkey Solutions
- Single point of responsibility from start to finish
- One purchase order
- Custom solutions to meet your needs
- 35+ years of experience
OUR CUSTOMERS SAY...
It's the gold standard. I look forward to doing additional business with you guys."
Everything working as it should!! Thank you."
Industries Served



















This is not a comprehensive list. If you don’t see your industry, give us a call.
LITERATURE
For access to downloads, line cards, case studies, manuals and more, please visit our resources page.








